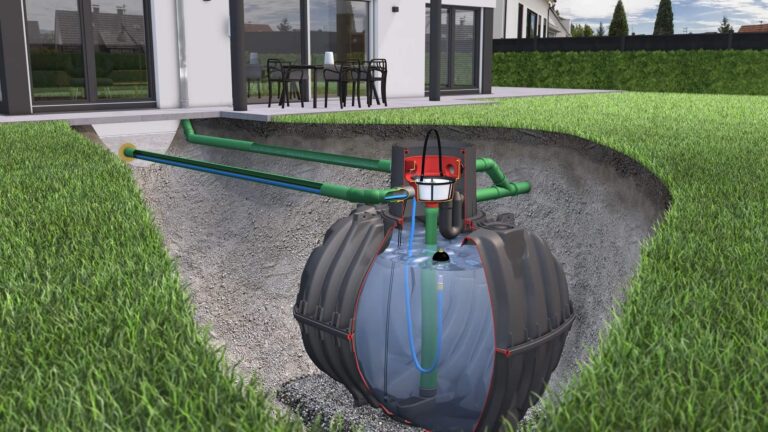
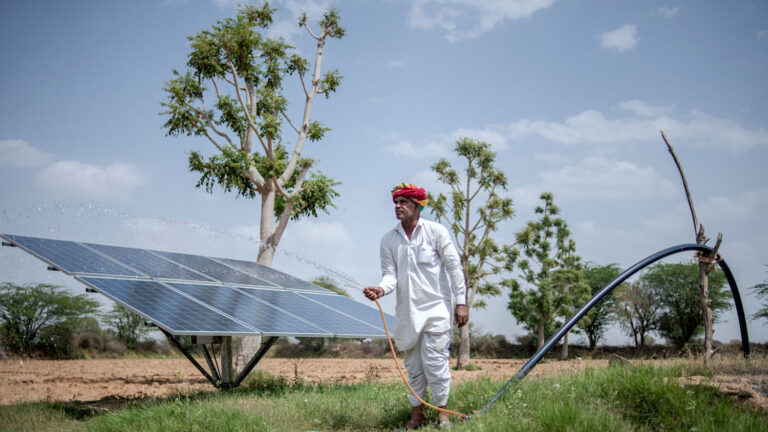
Solar water pumping systems provide an important solution for remote agricultural and community applications without access to electric grids. Where diesel or human-powered pumps were previously relied upon, solar technology offers a sustainable alternative.
A solar water pump works through the conversion of solar energy into electrical power. Photovoltaic panels collect sunlight and use the photovoltaic effect to generate electricity, charging an integrated battery bank. This stored energy then activates an electric motor coupled to a submersible or surface water pump.
Pumped water is typically transported to an elevated storage tank for gravity-fed distribution to end users. Since energy storage is not required during non-sunlight hours, the setup allows for continuous water delivery. Applications include irrigation, livestock watering, and drinking water supplies.
By replacing fossil fuel-burning pumps, solar pumping reduces carbon emissions and dependence on imported fuels. It also eliminates the physical labor previously needed for operation. This improved accessibility supports agricultural production and community development in remote regions previously unserved by infrastructure.
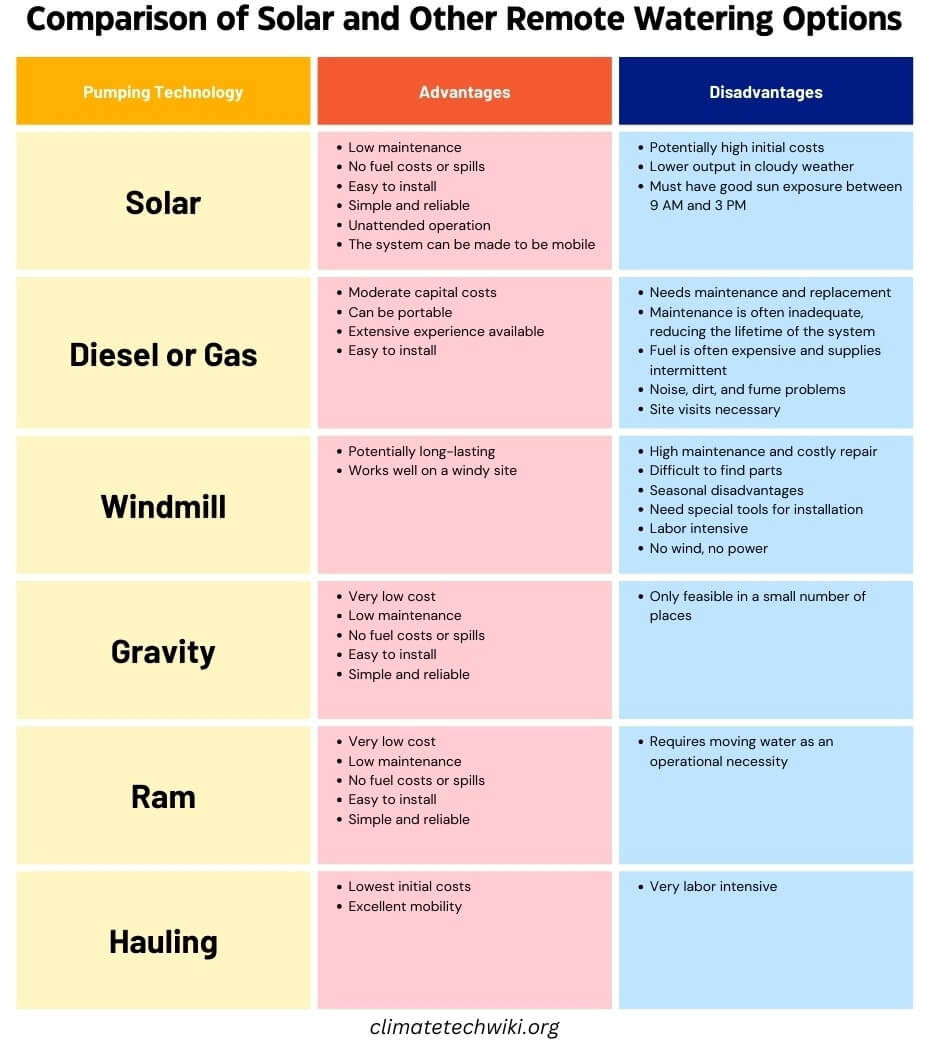
Feasibility of technology and operational necessities

When it comes to pumping water with the power of the sun, there are a couple of different options for how that pump works. The first is called a centrifugal pump. It uses fast spinning to suck water into the middle and fling it outward. Most regular electric pumps are like this.
The problem is, on cloudy days when the solar panels aren’t making as much juice, these pumps just don’t perform as well. Their speed drops way off. Not ideal when you need water all the time!
That’s where the positive displacement pump comes in. It uses something like a piston or screw to slowly and steadily move the water along. Not as fast as the other kind, but it can keep pumping just fine even with less power.
Since solar panels and batteries are expensive, pumps need to use the sun’s power as efficiently as possible. Positive displacement pumps tend to do that better since they keep working without missing a beat on overcast days.
When it comes to solar water pumps, there are two main types – submersible or surface. The kind you pick depends on where your water source is.
If you’re pumping from a well that’s underground, it makes sense to use a submersible pump since it can sit down in the well water. Surface pumps are better if you’ve got an open water source above ground, like a lake or stream.
Surface pumps are more affordable than submersible ones, but they have their limits. They don’t work as well for sucking water up from deep underground – about 6.5 meters is their max. But they shine at moving water over long distances above ground.
A floating surface pump is handy if your water source is a pond or lake. Just mount it right on top of the water. Submersible pumps need to be lowered down into a well, which makes installation a bit more involved.
Contribution of technology to social development
Solar pumps can make a difference for people living in rural areas. Where other ways of getting water might be unreliable, solar means they’ve always got access when they need it. That regular supply does wonders for public health.
It also leads to more time spent together as a community. Folks don’t have to travel as far each day to haul water back. That leaves more hours free for socializing and kids’ activities. As a result, whole communities become closer-knit with stronger bonds.
Some places even see fewer people moving away long-term because life’s a bit easier there now. When basic needs like water are met, it encourages putting down roots.
Contribution of the technology to protection of the environment

Once solar panels are up and running, they don’t need anything to keep producing electricity. No fuels being burned means zero waste or pollution from their day-to-day use. They’re also really quiet and still.
The biggest environmental effects come from making the panels at factories. Certain materials used in that process can be toxic if not handled properly. However, studies show solar creates much less pollution overall per unit of power compared to things like coal.
Most parts can also be recycled once panels reach the end of their life. Experts predict over 80% can be reused rather than thrown in the trash. Recycling solar gear is already financially viable too.
So in use, solar is clean and green. During construction, pollution can be an issue if safety rules aren’t followed. However the amount of damage is much smaller than fossil fuels. With recycling, solar has the potential to be an environmentally friendly energy source from start to finish if manufacturing keeps improving.
Using solar pumps instead of diesel or power from the electric grid has some real benefits for the climate. Those other options produce a lot of carbon dioxide as they run, either from burning fuel on-site or from the power plants supplying electricity.
Solar panels, on the other hand, don’t give off any greenhouse gases like CO2 when collecting energy from the sun. A solar water pump system runs completely emission-free.
If more farms and villages switched over to solar pumping, it could collectively save a ton of CO2 from entering the atmosphere. Every time one installation replaces a diesel motor or connects off-grid, it means less pollution.







